QGIS Plugin Development: Finding Nearest Neighbors
I described basics of vector layers manipulation in the previous part of the series. With my goal in mind (fully functional custom plugin capable of writing an attribute value from a source layer to a target layer based on a feature distance), I’d like to discuss spatial indexing and nearest neighbor analysis.
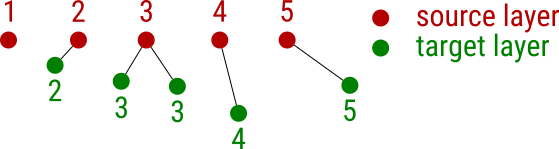
The picture above illustrates the task that can be solved solely by using QGIS API. Imagine you’re given a source layer with an attribute filled with values. You’re given a target layer as well, sadly though, the values in this layer are missing (not so rare in the GIS world, right?). Yet you know that the missing attribute value of each feature in the target layer can be filled by the value of its nearest neighbor from the source layer. How do you do that?
Generating dummy data
Let’s create two memory data sets with id and value attributes. Both of them will have ten features.
from qgis.core import QgsMapLayerRegistry, QgsVectorLayer, QgsFeature, QgsGeometry, QgsPoint, QgsSpatialIndex
from qgis.utils import iface
source_layer = QgsVectorLayer("point?crs=epsg:4326&field=id:integer&field=value:integer", "Source layer", "memory")
target_layer = QgsVectorLayer("point?crs=epsg:4326&field=id:integer&field=value:integer", "Target layer", "memory")
def create_dummy_data():
source_layer.startEditing()
target_layer.startEditing()
feature = QgsFeature(source_layer.pendingFields())
for i in range(10):
feature.setGeometry(QgsGeometry.fromPoint(QgsPoint(i, i)))
feature.setAttribute("id", i)
feature.setAttribute("value", i)
source_layer.addFeature(feature)
feature = QgsFeature(source_layer.pendingFields())
for i in range(10):
feature.setGeometry(QgsGeometry.fromPoint(QgsPoint(i + i, i)))
feature.setAttribute("id", i)
target_layer.addFeature(feature)
source_layer.commitChanges()
target_layer.commitChanges()
QgsMapLayerRegistry.instance().addMapLayer(source_layer)
QgsMapLayerRegistry.instance().addMapLayer(target_layer)
create_dummy_data()
Writing values from the nearest neighbor
The actual nearest neighbor analysis can be done in ten lines of code! First, the qgis.core.QgsSpatialIndex is built from all the source_layer features. Then, you iterate over the target_layer features and for each of them, gets only one (nearestNeighbor(f.geometry().asPoint(), 1)[0]) nearest neighbor. At last, you just write the nearest neighbor’s attribute value to the target layer and commit changes. Just use the following code with the code above.
def write_values_from_nn():
source_layer_index = QgsSpatialIndex(source_layer.getFeatures())
source_layer_features = {feature.id(): feature for (feature) in source_layer.getFeatures()}
target_layer_features = target_layer.getFeatures()
target_layer.startEditing()
for f in target_layer_features:
nearest = source_layer_index.nearestNeighbor(f.geometry().asPoint(), 1)[0]
value = source_layer_features[nearest].attribute("value")
target_layer.changeAttributeValue(f.id(), 1, value)
target_layer.commitChanges()
write_values_from_nn()
Missing pieces or what’s next
I’m one step closer to my goal. What’s missing?
- capabilities checks: does the target layer support edits? Check the layer data provider capabilities to find out.
- user logging: notices, warnings or errors are completely missing. It will be great to have them shown inside
qgis.gui.QgsMessageBar. - custom attributes: this version expects both layers to have the same attribute with the same data type.
- GUI: a very simple PyQt widget will turn this console-based script into a custom plugin. That’s what’s going to be next.